Creating a New Custom Report
Custom Reports are created from templates located on the Custom Reports page. See Creating a New Custom Report Template and Editing a Custom Report Template for instructions on how to create and modify templates.
1. Navigate to the SpecConnect Reports page by pressing the Reports (pie-shaped) icon from the options on the left side of the SpecConnect web page.
2. Press the New Report button.
3. In the New Custom Report screen, enter a name for the report. Select the station and template from the Default Equipment and Template menus respectively.
4. Press the Save and Edit Sensors button.
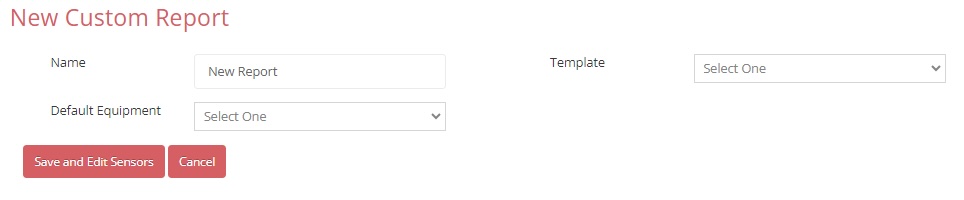
5. In the Edit Custom Report screen, select the specific port for the sensor which will be used to calculate the values for that column. Often, there will only be one choice. But, if the device has more than one sensor of a given type, the correct port must be identified. One example of when this distinction is important is for stations with both air and soil temperature sensors. Although a default station has been selected, it is possible for any individual column to report data from a different station. Pressing the station name (inside black boxes in image below) will bring up a dropdown menu with other available stations.
The station, template, and sensor designations are now set. Press the Save & Return to Reports button to return to the Reports page. This is where the date range will be selected.
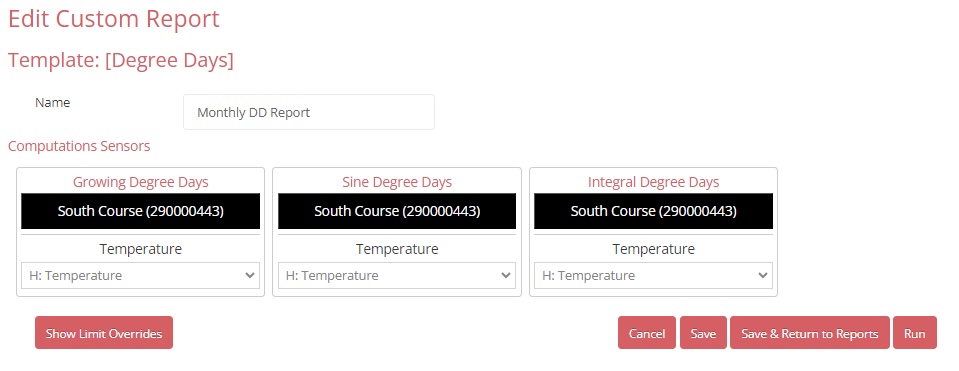
6. The report appears in the Custom Reports section. Press the name of the report

7. Use the dropdown menus to select the date range and time interval for the report.
8. Press the Run button to generate the report.
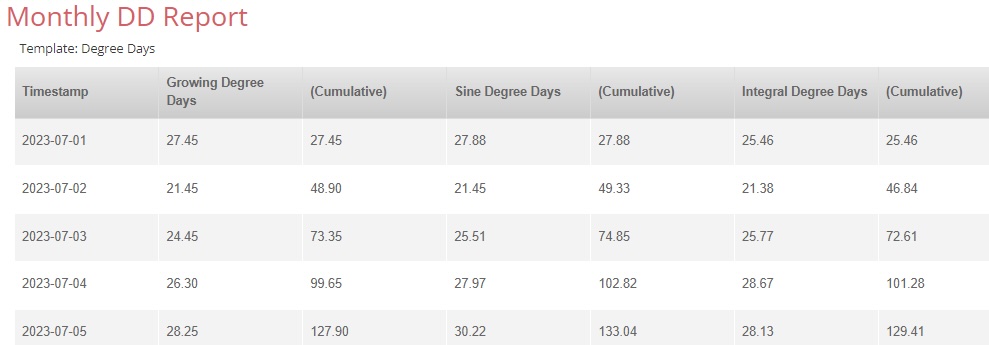
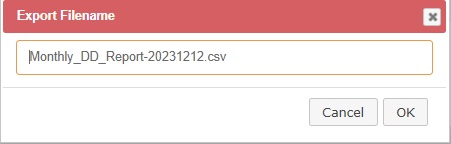
9. There is an option to export the data to your PC. Press the Export button to initiate the process. SpecConnect will offer a default name for the exported file. This can be edited. The file will be saved to your PC’s Downloads folder.
Creating a New Custom Report Template
1. Navigate to the SpecConnect Reports page by pressing the Reports (pie-shaped) icon from the options on the left side of the SpecConnect web page.
2. Press the New Template button.
3. Enter the name of the template and press the Create Template and Add Columns button.
4. The contents of the columns need to be defined. Press the Add Column button to configure the next column.
5. From the dropdown menu, select the sensor for this column.
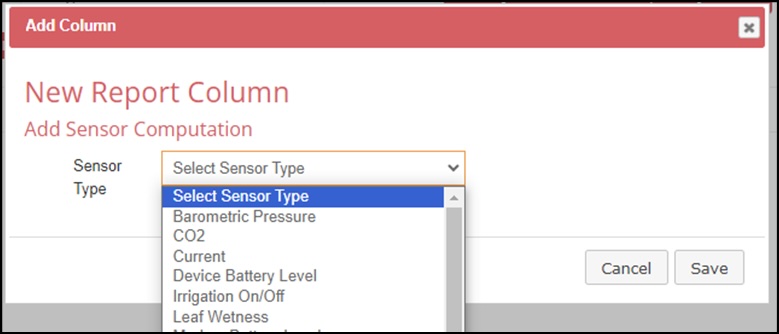
6. Select what computation will be displayed for this column.
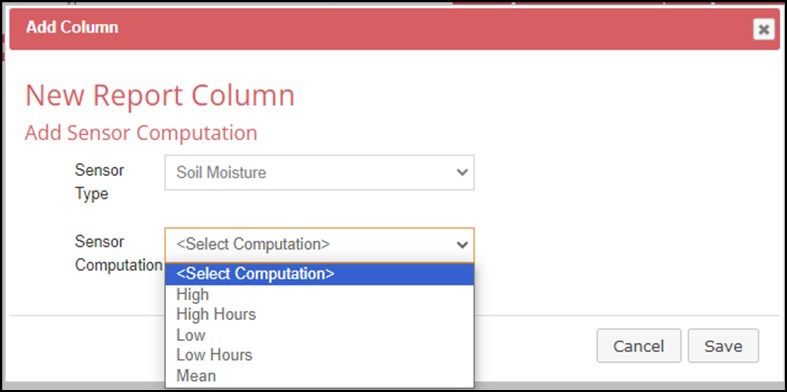
7. A default title is generated for the column header. This can be edited. Some computations allow for an optional additional column with supplemental information. See Glossary for more information on the terms shown below.
Time: Available with High and Low Display options, creating an additional column indicating when the respective high or low value occurred.
Cumulative: Available with Sum, Flow, Hrs, HiHrs, LoHrs, and Degree Day display options. It creates an additional column showing a running total of the accumulation of the desired parameter up to, and including, the displayed day.
Total: Available with Sum, Flow, Hrs, HiHrs, LoHrs, and Degree Day display options. It creates an additional line at the end of the report showing the sum of the desired parameter over the entire time range under consideration.
Press Save when finished.
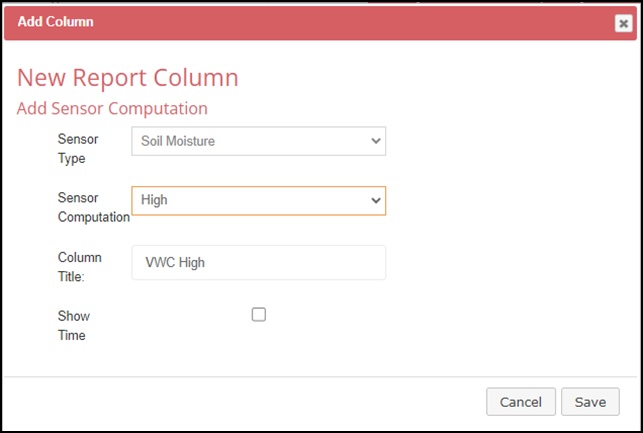
8. The current column definitions will be displayed. Once defined, a column can be deleted. Column configurations, however, cannot be edited.
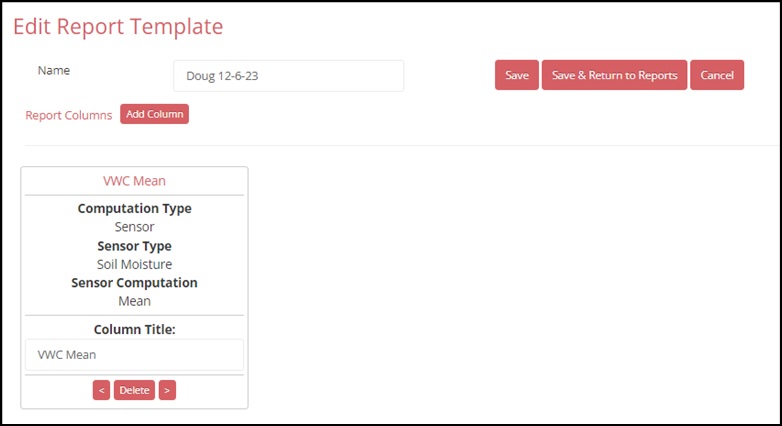
9. Repeat steps 4 to 7 to create additional columns in the template. The report that is generated based on this template is a table. If you wish to change the order of the columns, press the < or > buttons to shift the columns to the right or left.
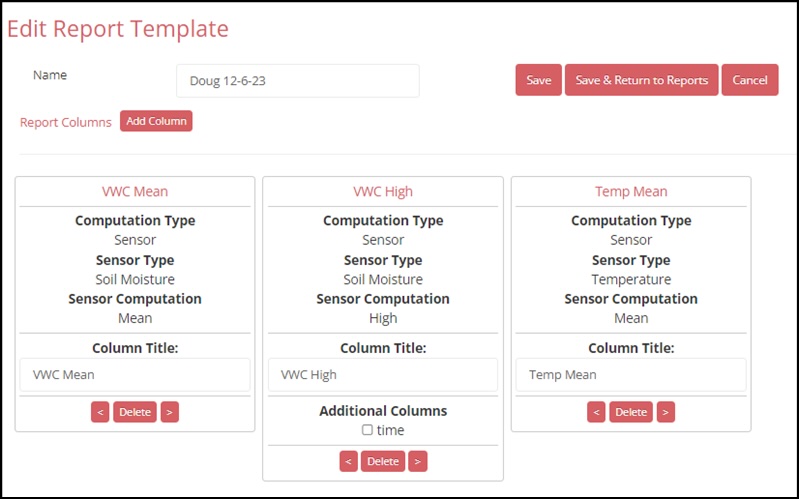
10. When the template contains all the desired columns, press the Save & Return to Reports button. This will return you to the main Reports page. The newly created template will appear along with the Master Custom Report templates. User created templates will have both an Edit and a Delete button.

Editing a Custom Report Template
There are 3 types of Custom Report templates that can be edited before creating a Custom Report.
User Created Template (see Creating a New Custom Report Template). These templates have an Edit and Delete option.
Master Template. These are default templates that come automatically with SpecConnect. The titles of these templates have an asterisk (*). Master templates only have an Edit option. Custom reports can be generated (see Creating a New Custom Report) directly from these templates. But they can also be used as starting points to create a new Custom Report template.
Shared Template. If a SpecConnect account has multiple users, each user can create new templates. By default, the template is only available to the person that created it. However, there is an option to share the template. The options for working with Shared templates are the same as for Master Templates.
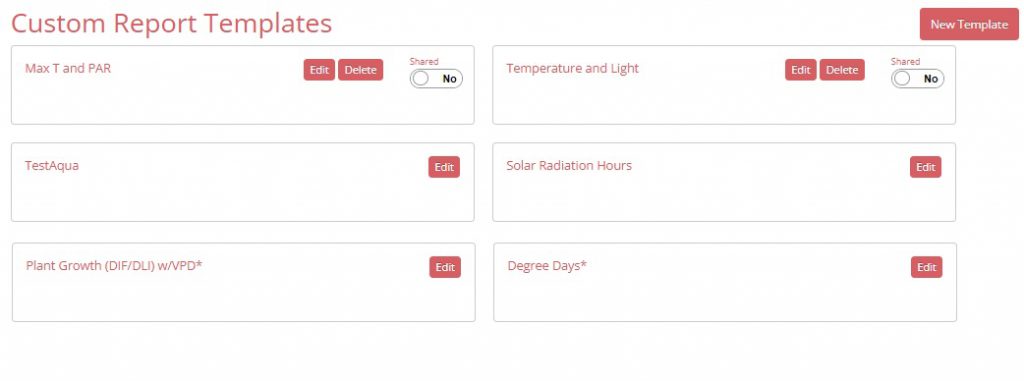
1. Navigate to the SpecConnect Reports page by pressing the Reports (pie-shaped) icon from the options on the left side of the SpecConnect web page. Scroll down to the Custom Report Templates section.
2.Press the Edit button for the template you wish to modify. If this is a template you created, you are simply editing and saving the template parameters. For Master and Shared templates, SpecConnect will inform you that you are creating a copy of the template. The default name assigned to this template will reflect that (see image below). This name can be changed. At this point columns can be added or deleted in the same way as for newly created Custom Report templates (see Creating a New Custom Report Template).

Glossary
Mean: The average value within a dataset, indicating the central tendency of a parameter over a specified time range.
High: The maximum value of a parameter during a defined time period, identifying peaks in the dataset.
Low: The minimum value of a parameter within a specified time period, aiding in the identification of troughs in the dataset.
Chill: Refers to the calculation of total chill hours, a crucial metric for evaluating environmental conditions. Chill hours are determined by measuring the duration spent below a designated base temperature while remaining above a defined lower limit. This metric holds significance in assessing the fulfillment of specific chilling requirements essential for optimal growth and development of crops or plants.
Fruit trees need cold weather to produce fruit in the spring. Different fruits have different chilling thresholds. If they don’t get enough cool weather over the winter, a chemical spray can be used to encourage fruit production.
ChUtah (Utah Chilling Units): This calculation method applies different weights or units to chilling hours, recognizing that not all hours have equal impact. It factors in temperature variations, assigning units based on hourly temperature readings.
DM/CP (Dynamic Chilling Portions): This calculation method applies different weights or units to chilling hours, recognizing that not all hours have equal impact. It factors in temperature variations, assigning units based on hourly temperature readings.
Diff: Diff is the difference between the average day and night temperatures. Diff uses a PAR sensor to tell the difference between day and night.
Hrs: In SpecConnect, “Hrs” represents the display of the amount of time a selected sensor measured values above a user-defined threshold. This information is entered in the same section where base temperature and upper limit details are provided for degree day reports.
DD, ADD, GDD, DDSine: These options, exclusive to temperature data in SpecConnect, display the number of degree days accumulated for the day based on user-defined base temperature and upper limit.
• DD: Degree Days.
• ADD: Actual Degree Days.
• GDD: Growing Degree Days.
• DDSine: Single Sine Method.
Flow: An option available for data from the Irrigation On/Off sensor in SpecConnect. It displays the total amount of irrigation water applied during the day, based on the user-entered irrigation system flow rate.
HiHrs and LoHrs: Exclusive to soil moisture data in SpecConnect, these options display the amount of time the selected soil moisture sensor was above (HiHrs) or below (LoHrs) a user-defined threshold value
For a visual walkthrough and more detailed instructions, you might find the following video tutorial helpful: SpecConnect Reports
